Table of contents
Introduction
In today's digital era, where organizations rely heavily on cloud-based applications, remote branches, and distributed workforces, the demand for reliable and efficient network connectivity has skyrocketed.
Traditional Wide Area Networking (WAN) architectures, while once effective, are struggling to keep up with the evolving needs of businesses.
Enter Software-Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN), a revolutionary technology that addresses the limitations of traditional WAN and unlocks a new realm of possibilities for network management.
In this blog post, we'll explore why SD-WAN has become the go-to solution for modern networking and how it resolves the congestion and related issues faced by traditional WAN, using the example of MPLS traffic routing through the Hub site for internet access.
The Limitations of Traditional WAN
For example, Traditional WAN architectures, often built on Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS), were designed for a different era where most applications and resources were housed in centralized data centers.
However, with the shift to cloud computing and the increasing reliance on internet connectivity, traditional WAN architectures face several challenges. One such challenge is the congestion and related issues caused by routing MPLS traffic through the Hub site for internet access.
Example 1: Congestion, Performances
MPLS Traffic Routing Through the Hub Site
In a traditional WAN setup, branches typically rely on MPLS connections to access both corporate resources and the internet. This approach involves routing all traffic, including internet-bound traffic, through the Hub site before reaching the internet gateway. This centralized traffic flow can lead to congestion and performance issues.
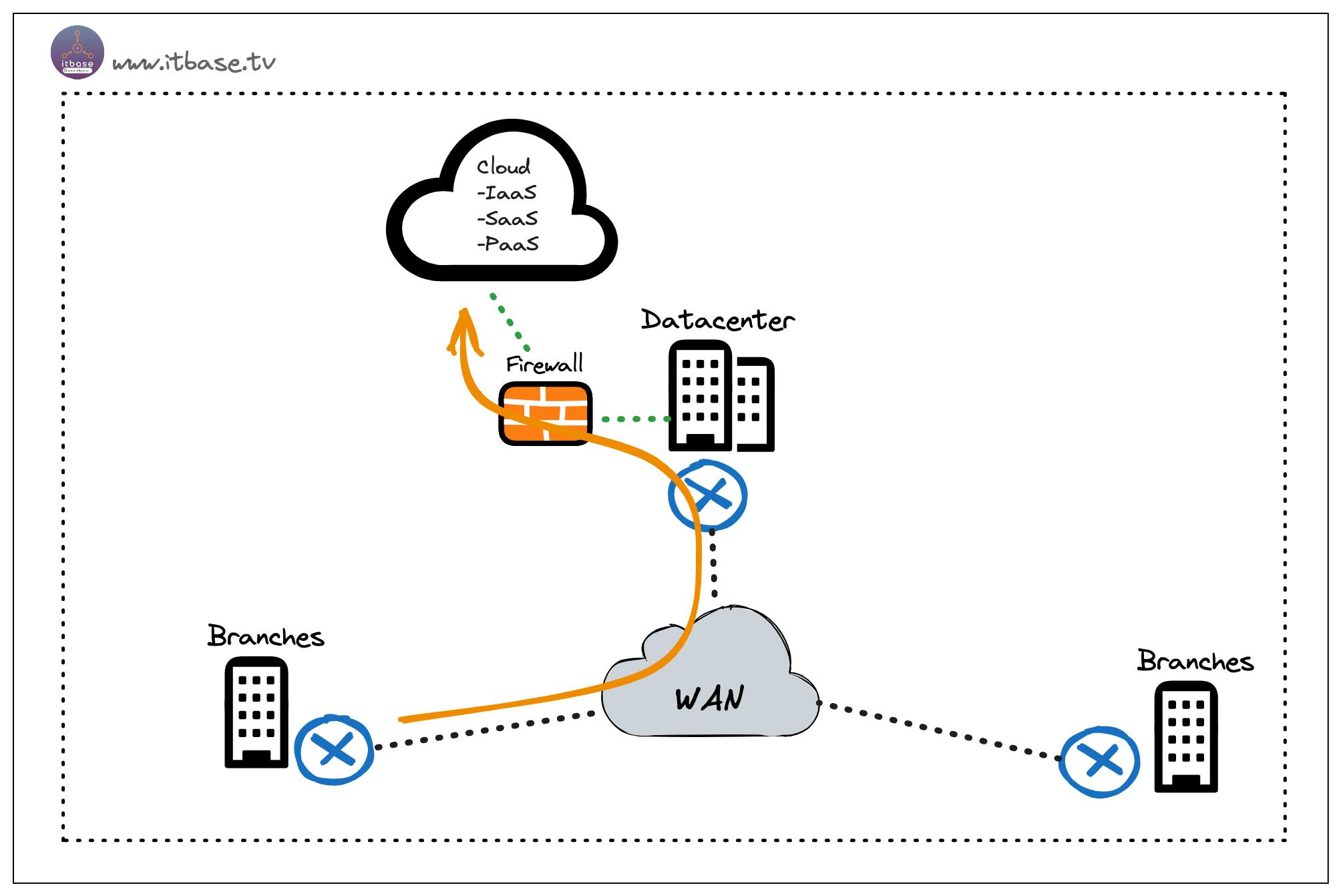
When internet-bound traffic from multiple branches is funneled through the Hub site, it creates a bottleneck that affects the overall network performance.
The Hub site becomes a single point of failure, and any network issues or congestion at the Hub site can impact the performance of all connected branches. Additionally, the Hub site's internet bandwidth may not be sufficient to handle the aggregated traffic, leading to latency and poor user experience for branch users accessing cloud-based applications or web services.
SD-WAN Resolving Congestion with Direct Internet Access
SD-WAN addresses the congestion and related issues of traditional WAN by introducing a concept known as Direct Internet Access (DIA). With SD-WAN, branches can access the internet directly, bypassing the need to route all traffic through a central Hub site.
This distributed architecture improves performance and reduces latency by providing branch users with localized internet access.
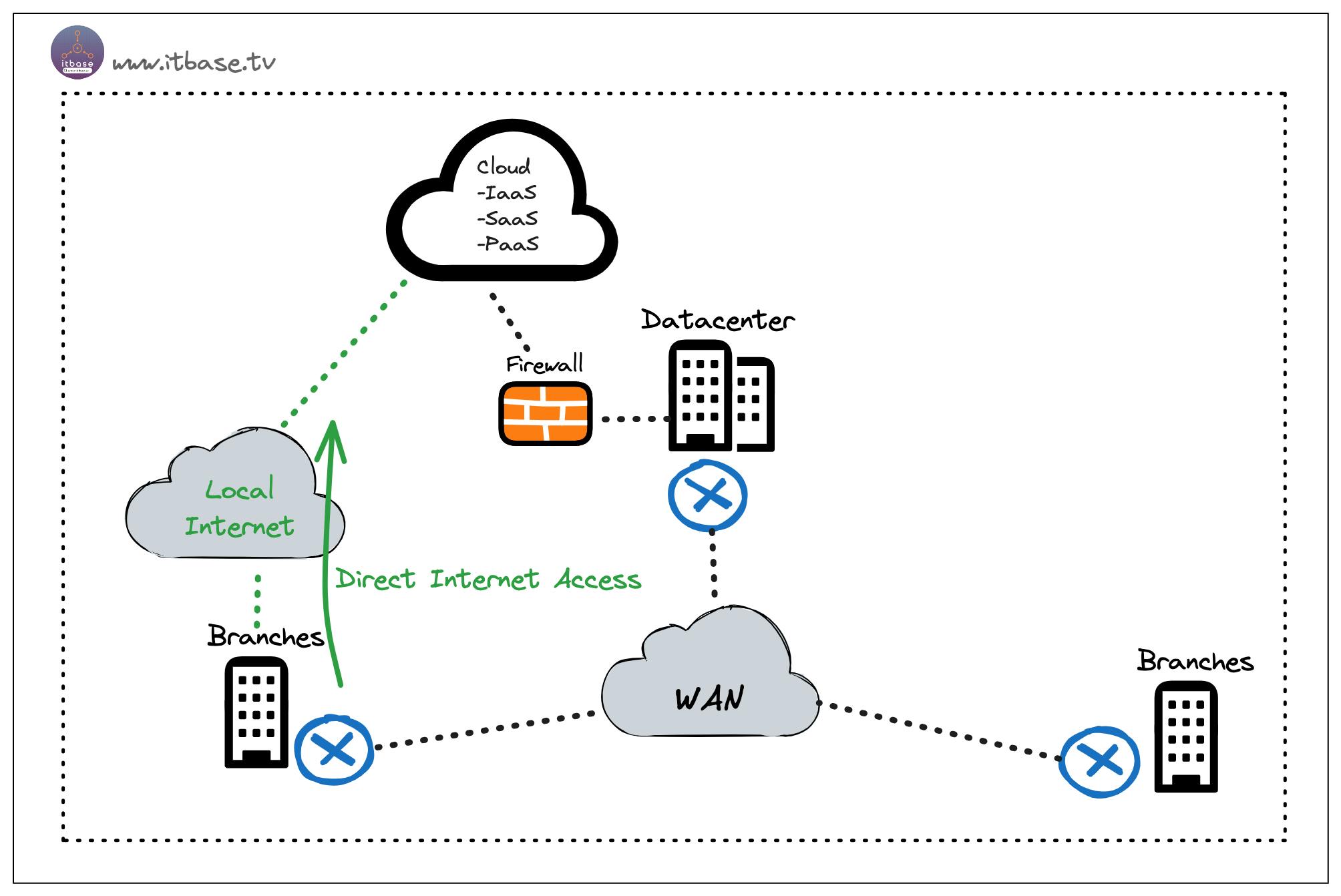
By leveraging DIA, SD-WAN allows branch traffic to be intelligently routed based on application requirements and network conditions. Internet-bound traffic can be securely directed to the nearest internet breakout point, such as a local internet service provider (ISP) or a cloud-based security service, optimizing the network path and reducing latency.
This approach also offloads the Hub site from unnecessary traffic, enabling it to focus on mission-critical functions.
Example 2: Management Challenges
Challenge of Traditional WAN - Growing Number of WAN Edge Devices
In traditional WAN architectures, the number of WAN edge devices increases as the organization expands its network and adds more branch locations. Each branch typically requires a router or other networking equipment to connect to the WAN. With traditional WAN, managing a growing number of WAN edge devices poses several challenges:

Manual Configuration and Management: Traditional WANs often rely on manual configuration and management of individual devices. As the number of devices increases, it becomes increasingly time-consuming and prone to human errors. Managing configurations, firmware updates, and troubleshooting across numerous devices becomes a daunting task.
Lack of Centralized Control: Traditional WAN architectures lack centralized control and visibility, making it difficult to enforce consistent policies and ensure network-wide security. Network administrators must individually configure and monitor each device, leading to inconsistency and potential security vulnerabilities.
Limited Scalability: As the number of WAN edge devices grows, scalability becomes a concern. Traditional WAN architectures may struggle to handle the increased traffic and demand, resulting in performance issues and slower network speeds. Adding new devices or scaling the network becomes cumbersome and time-intensive.
SD-WAN Benefits in Solving the Management Challenges
SD-WAN addresses the management challenges associated with a growing number of WAN edge devices by providing centralized control, automation, and scalability. Here's how SD-WAN benefits solve these challenges:

Centralized Management and Orchestration: SD-WAN offers a centralized management and orchestration platform that provides a single pane of glass for network administrators to configure, monitor, and manage the entire WAN infrastructure. Policies can be easily defined and applied network-wide, ensuring consistent configurations and enhancing security.
Automation and Simplified Operations: SD-WAN leverages automation to streamline operations and reduce manual configuration tasks. Network-wide policies can be implemented and updated with ease, eliminating the need for individual device configurations. This simplifies the management process, reduces human errors, and increases operational efficiency.
Scalability and Flexibility: SD-WAN architectures are designed to scale seamlessly as the network grows. New branch locations and WAN edge devices can be added effortlessly, and configuration changes can be pushed out quickly through the centralized management platform. SD-WAN also enables dynamic path selection and load balancing, optimizing traffic across multiple links for enhanced performance and scalability.
Enhanced Visibility and Monitoring: SD-WAN solutions provide robust visibility and monitoring capabilities, offering real-time insights into network performance, application usage, and security threats. Administrators can proactively identify and troubleshoot issues, ensuring optimal network performance and minimizing downtime.
Conclusion
SD-WAN has emerged as the preferred solution for modern networking due to its ability to overcome the limitations of traditional WAN architectures. It addresses congestion, performance, management challenges, and provides enhanced visibility and scalability.
However, it is important to note that traditional WAN still has its place and continues to be used by many organizations for critical traffic. In certain scenarios where stringent security or specific requirements are necessary, traditional WAN architectures may still be the preferred choice.
Each organization needs to evaluate its unique needs and requirements to determine the most suitable approach. While SD-WAN offers numerous advantages, it is essential to recognize that traditional WAN still plays a significant role in supporting critical traffic for many corporations.
The decision between SD-WAN and traditional WAN should be based on a careful analysis of business needs, network requirements, and security considerations.
My name is Nam who loves to talk and share knowledge related to Networking, Automation, and so on. More about me: nam-nguyen.me
Hope you enjoy the blog and don't forget to join the Tech-Learner-Hub to get more and more valuable content.

